For many people, the iPhone 12 effectively disappeared from the market on Tuesday, when Apple introduced iPhone 15 models and stopped selling the 12, first released in October 2020. In Europe, however, the iPhone 12 remains a notable device, as a number of countries are following France’s lead in looking into the device’s electromagnetic profile.
What kicked off the unexpected concern about a nearly three-year-old phone was France’s National Frequency Agency (ANFR). On the same day as Apple’s fall product announcements, the ANFR informed Apple that the iPhone 12 exceeds EU regulations for Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), the rate at which a human body would absorb radiation from a device. A translated version of the ANFR report has the agency calling on Apple to withdraw the iPhone 12, “quickly remedy this malfunction,”and if not, “recall copies already sold.”
There are two measures of SAR for a device operating in the same frequency range as an iPhone, per EU standards. The “head and trunk”value, taken to protect against “acute exposure effects on central nervous tissues”when a phone is against the head or in a pants pocket, must not exceed 2 Watts of power per kilogram of body tissue, averaged over six minutes. When the phone is held in the hand or in clothing or accessories, for a “limbs”value, it’s 4 W/kg.
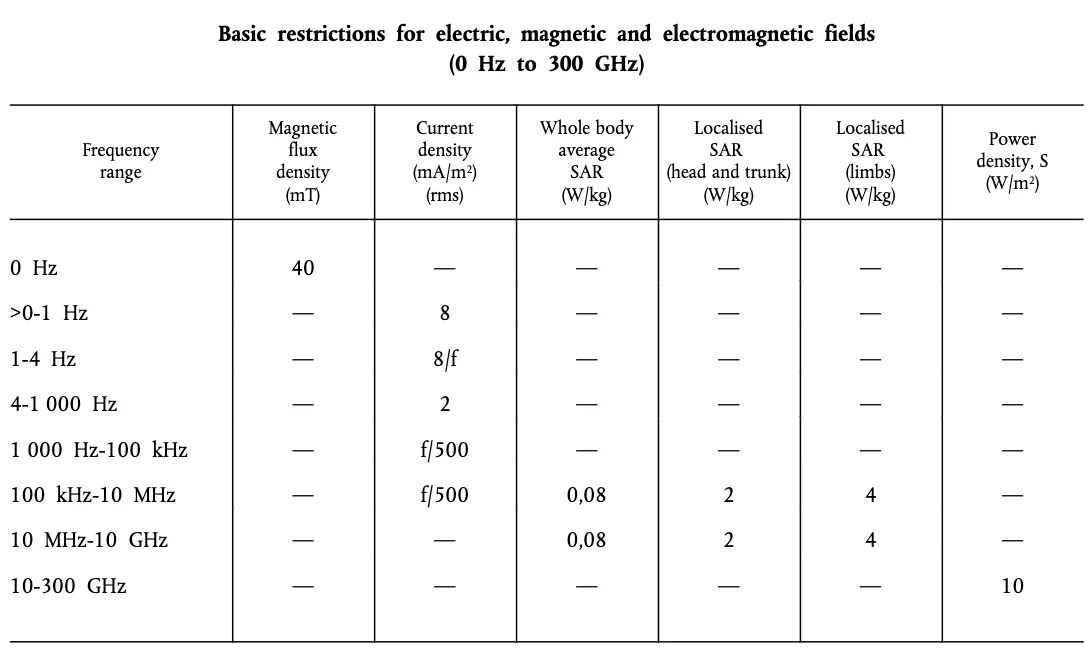
France’s ANFR measured the iPhone 12 exceeding the “limbs”limit at 5.74 W/kg. The ANFR stated that it would ensure the iPhone 12 was no longer available for sale in France and would oversee “corrective updates”it expects from Apple. Jean-Noel Barot, a digital and telecommunications minister in France, told newspaper Le Parisien that software updates could fix the issue, according to Reuters.
Apple responded swiftly to ANFR’s claims, telling multiple press outlets earlier this week that the iPhone 12 was certified by multiple international bodies and that it had provided the ANFR with documentation showing the device within regulatory limits, both from within Apple and independent lab results. Ars Technica reached out to Apple for comment and will update this post with new information.
The EU’s standards note that within a phone’s typical frequency range, the main danger of excess radiation is not changes to cells or chemicals in the body, leading to cancer, but “whole-body heat stress and excessive localised [sic] heating of tissues.”The vast majority of mobile phone research indicates no adverse effects from regular exposure to the non-ionizing frequencies phones use to communicate. But a series of studies, however inconclusive or problematic, have raised unnecessary concern and garnered media attention. The World Health Organization states that “no adverse health effects have been established as being caused by mobile phone use.”
France’s notice has spurred action by other countries. Germany’s Federal Office for Radiation Protection said Wednesday that “the question of the need for change is currently the subject of discussions,”Reuters reported. Belgium’s state secretary for digitalization, Mathieu Michel, told Reuters that he reached out to regulators to review not just the iPhone 12, but all Apple smartphones and other devices. Denmark and Italy have said they are investigating but have taken no formal actions.
In the US, SAR limits set by the Federal Communications Commission are 1.6 W/kg. The iPhone 12’s submitted SAR levels were measured at 1.554 W/kg at their peak, generally when using a hotspot or engaging in “Simultaneous Transmission.”The iPhone 12 did, of course, clear the FCC for release in 2020.
French regulators have recently shown a noted enthusiasm for demanding more from US-based tech companies. They’ve asked Google and Facebook to offer one-click cookie rejection and put repairability scores on smartphones and appliances and told the US and other nations that they want to see global AI regulations by year’s end.


