Today AMD released further information about its new Ryzen 7040U family of laptop chips, which integrate the RDNA 3 integrated graphics and Zen 4 CPU architecture into thin and light laptops. The 7040U CPUs will be the ones to hold out for if you want to maximize performance without upgrading to a larger laptop with a dedicated GPU, even if they are only a part of AMD’s (sometimes confusing) Ryzen 7000 laptop series.
The release of these processors has been postponed twice by AMD. Although AMD stated in mid-March that systems would start shipping in April, it is now the first week of May. Although the larger PC manufacturers will probably be able to get things to market a little bit sooner, Framework, one of the laptop manufacturers offering a Ryzen 7040-series laptop, won’t actually be shipping its preorders until sometime in Q3.
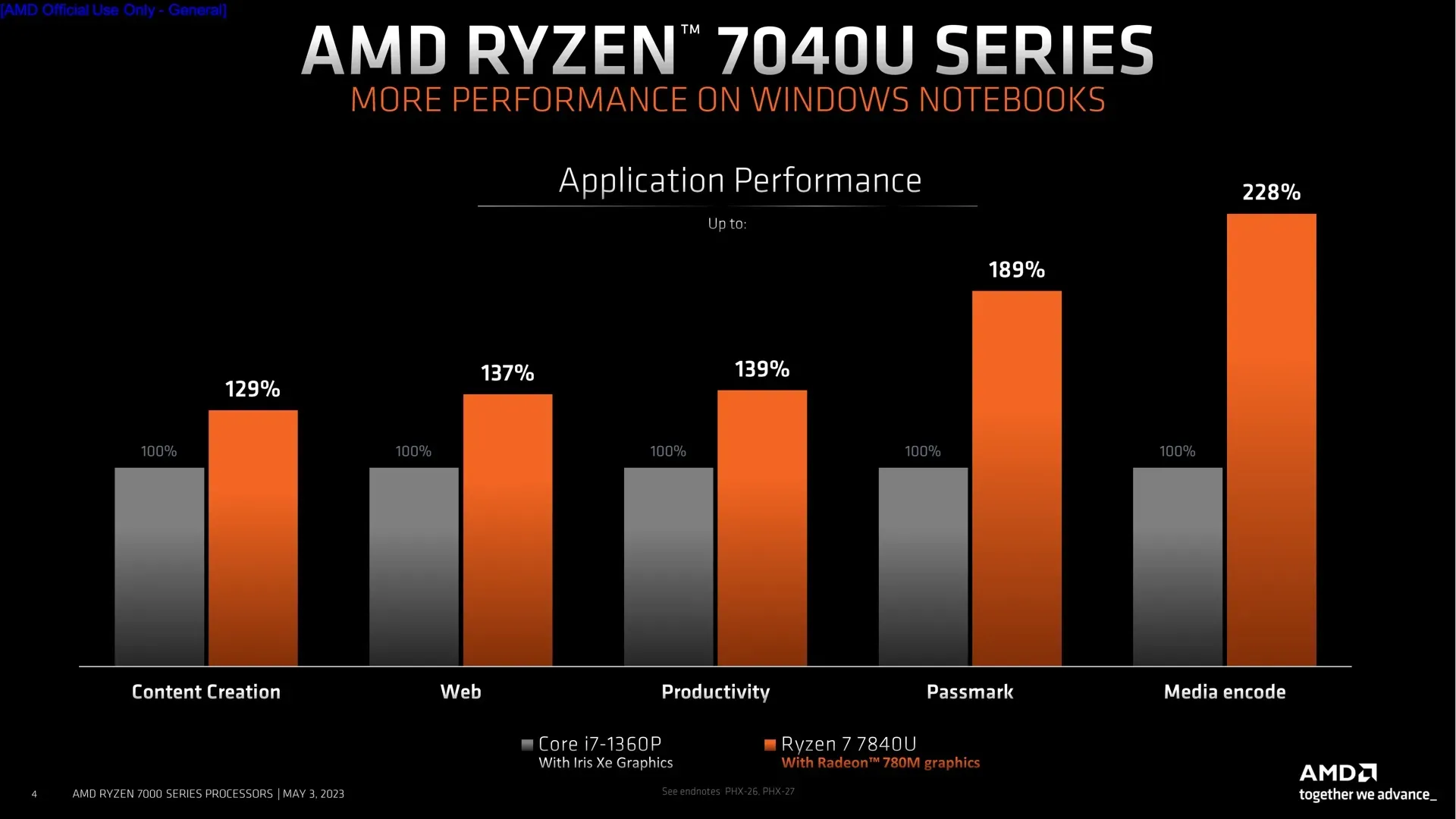
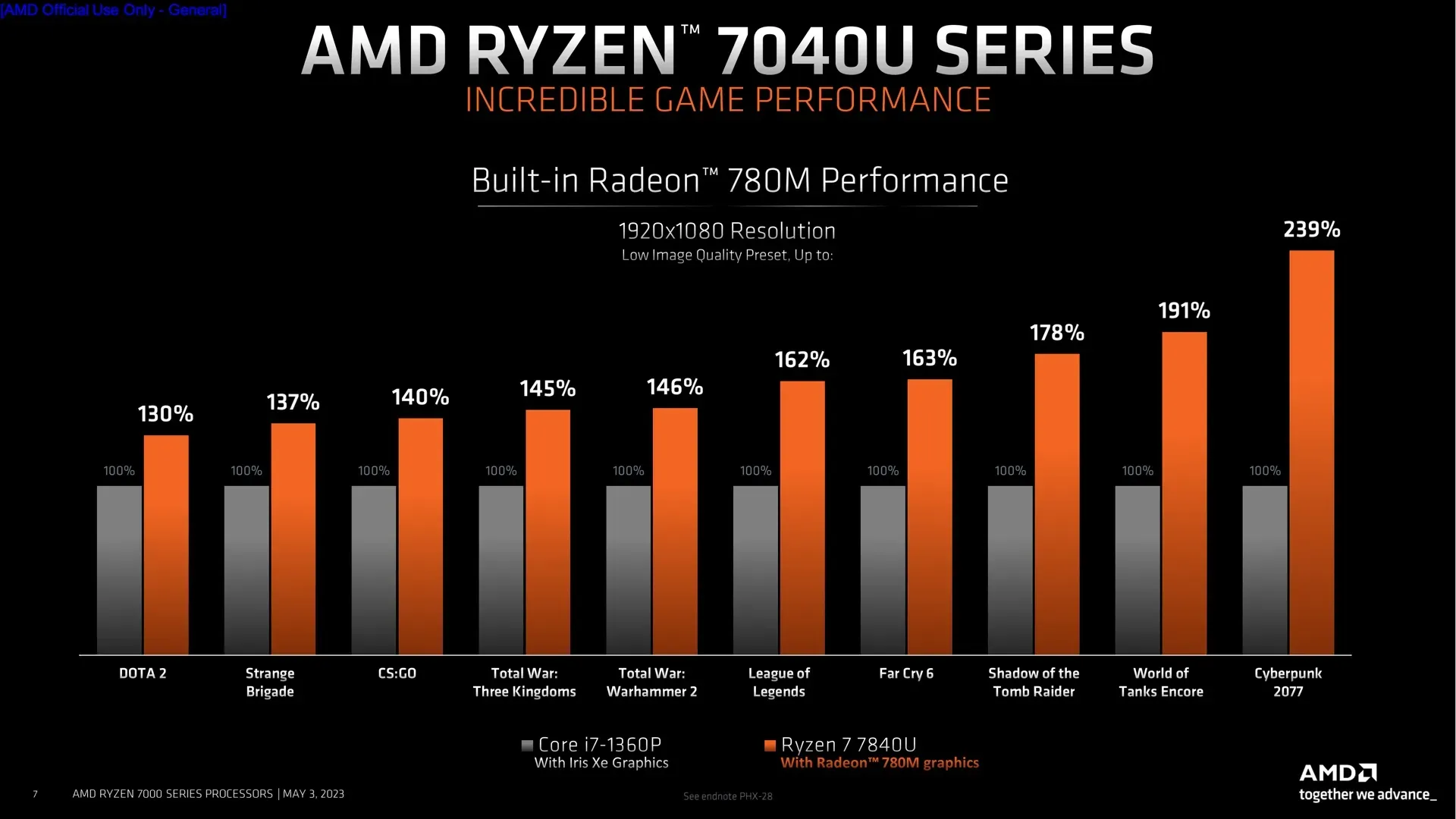
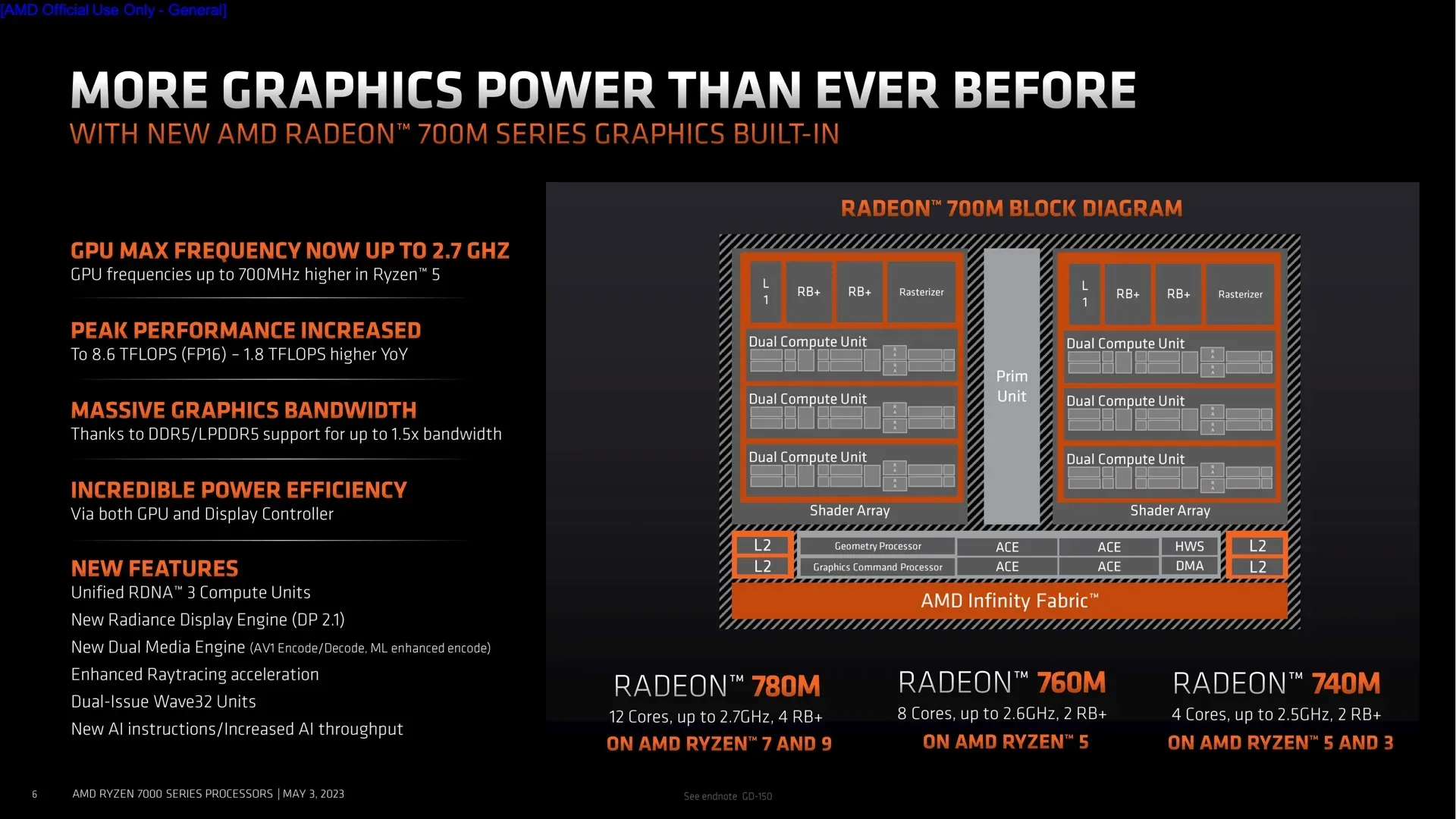
The enhanced CPU and GPU performance of the Ryzen 7040 chips is the most important feature for the majority of programs and games. The top-tier Ryzen 7 7840U combines a Radeon 780M GPU with 12 RDNA 3 cores with 8 CPU cores operating at up to 5.1 GHz. The Radeon 760M GPU has 8 cores, and the Ryzen 5 7640U has 6 CPU cores that can run at up to 4.9 GHz. While the Ryzen 3 7440U combines the same Radeon 740M GPU with 4 CPU cores, the Ryzen 5 7540U has the same 6 CPU cores but a lower-end Radeon 740M GPU with 4 cores.
The TDP of each of the four Processors ranges from 15 to 30 W. Based on how quickly they want their computers to operate and how much heat their fans and heatsinks can dissipate, manufacturers can choose what TDP to employ.
The Ryzen Z1 Extreme and Z1 processors that AMD unveiled for portable gaming PCs last week bear a striking resemblance to the 7840U and 7540U, and thanks to that announcement, we know that increasing the number of GPU cores from 4 to 12 does not always quadruple or even double performance. Even the entry-level Radeon 740M should be an improvement over the three-generation-old Intel Iris Xe GPU that Intel still employs for its ultrabook processors because memory capacity is still a big barrier for integrated GPUs.
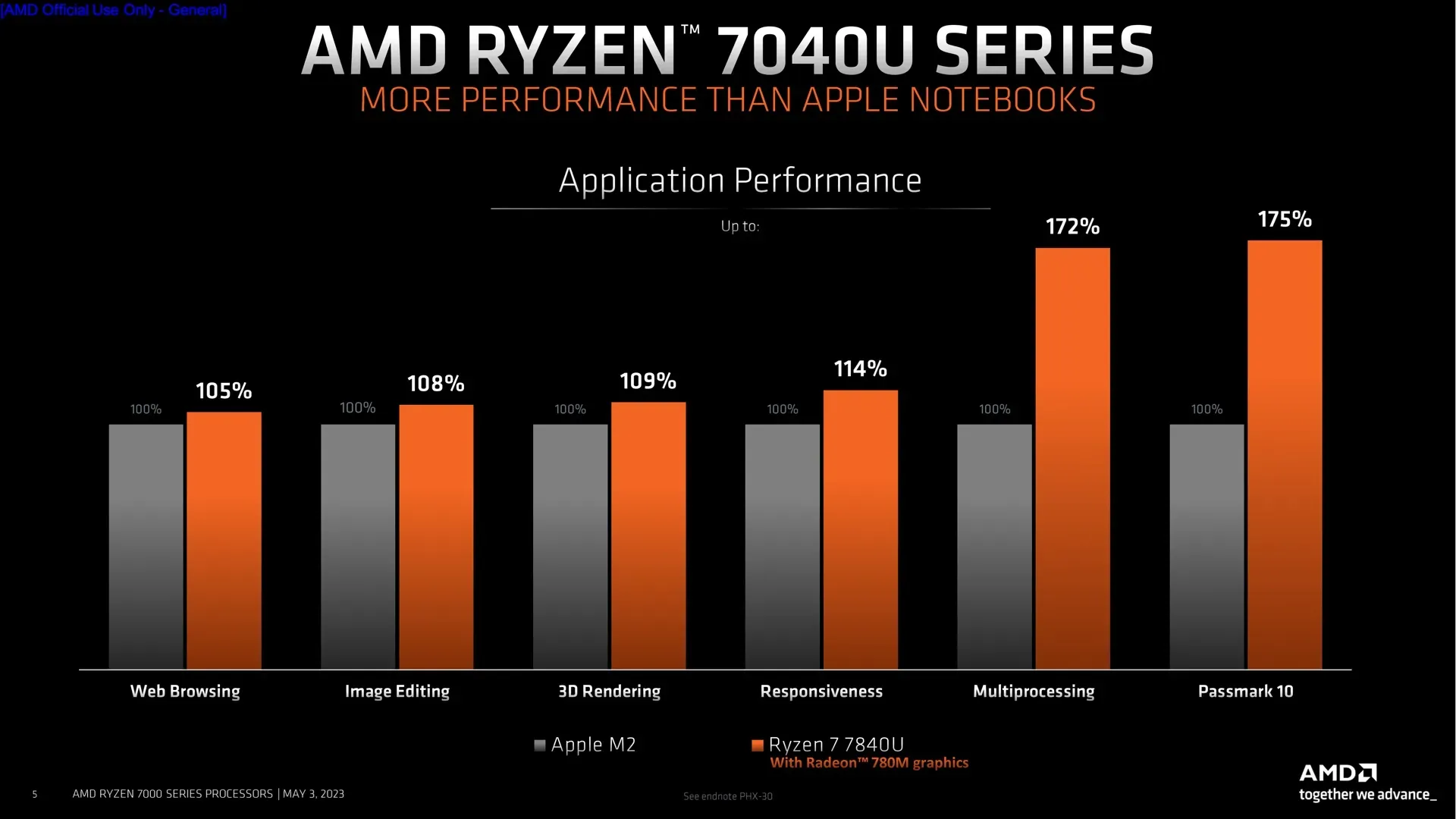
Regarding performance, AMD claims that the 7840U can outperform both the Core i7-1360P and Apple’s M2 in a few key areas. It’s odd that the business didn’t compare the 7840U to the Core i7-1370P, which is the fastest CPU made by Intel in this product category and has two more P-cores than the i7-1360P. AMD’s performance comparisons should be taken with a grain of salt, but Ryzen’s performance should still be competitive.
In addition, the 7840U and 7640U now have a new feature called «Ryzen AI,» which, as the name suggests, is hardware designed specifically to speed up AI and machine-learning workloads (Apple’s «Neural Engine» serves a similar purpose in the M1 and M2 CPUs). AMD’s XDNA architecture, which it created after buying Xilinx, powers Ryzen AI. «The first specialized artificial intelligence hardware in an x86 processor,» according to AMD, is Ryzen AI. Although they won’t be available until later this year at the earliest, Intel’s next-generation chips, code-named Meteor Lake, are rumored to include AI acceleration.
When you run workloads locally rather than on a server, Ryzen AI should enhance the performance of things like AI-powered language models, image generation, and voice transcription. A few AI-accelerated capabilities are already included in Windows 11, such as «Studio Effects» for cameras that may change your background and apply other effects. Since their Qualcomm Snapdragon-based processors include «neural processing units» (NPUs), which the majority of current x86 processors lack, these are currently mostly exclusive to Arm-based Windows hardware like the Surface Pro 9 with LTE or the Windows Dev Kit 2023.
As more PCs are equipped with the necessary hardware to benefit from them, Windows and other operating systems will probably start to incorporate more AI-powered features.
Listing image by AMD


