Processors based on AMD’s new Zen 4 architecture won’t arrive until this fall, but the company is already hinting at what’s to come. As reported by AnandTech, AMD is planning a new Zen 5 architecture, which is currently due on both desktop and laptop PCs sometime in 2024. remain on track to launch in 2022.
AMD also provided more information on Zen 4 performance. The company said at Computex that the Ryzen 7000 series chips will have approximately 15% higher single-thread performance than the Ryzen 5000. This is for most of the speed improvement, while the remaining 5-7 percent will come at the expense of higher clock speeds for Ryzen 7000 processors. Zen 4 can also deliver about 25 percent higher performance per watt than Zen 3.
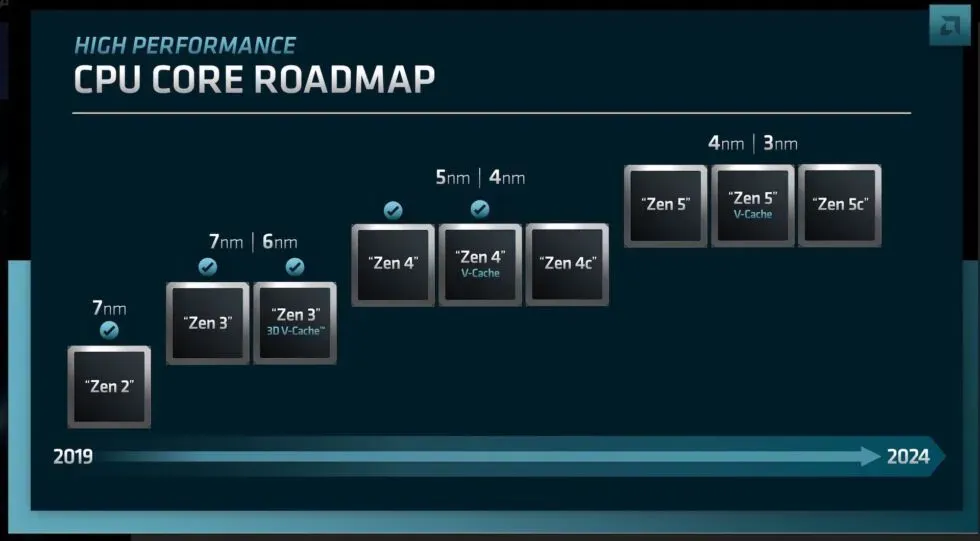
The company will also be bringing back its 3D V-Cache technology for select Zen 4 processors. This allows AMD to place an additional L3 cache on top of the CPU die, providing a significant increase in cache capacity without increasing the footprint of the CPU die or CPU package. As we saw in our Ryzen 7 5800X3D review, this technology helps with gaming performance in particular, though the chip also ran a bit warmer than Zen 3 processors without 3D V-Cache, and its slightly lower clock speeds made it run faster. slightly worse in non-gaming workloads.
We didn’t know if 3D V-Cache would be a feature on all Zen 4 processors, but AMD’s slide makes it clear that Zen 4 processors will be available with and without additional cache. As in the case of the 5800X3D, chips with 3D V-Cache are likely to be aimed primarily at gamers, since these are the applications that bring the greatest benefit.
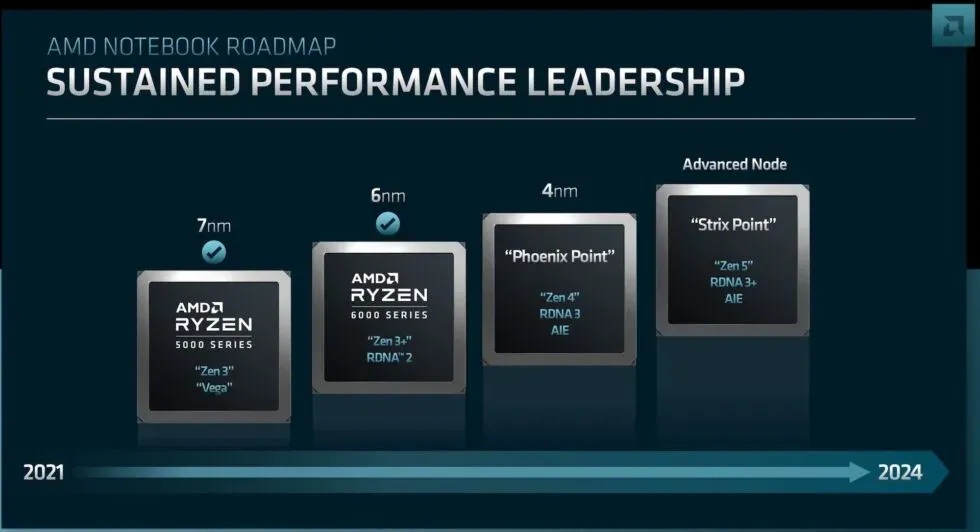
As for next year’s Zen 4-based laptop chips, AMD’s laptop processors have always been a bit different from desktop processors, with monolithic chip designs instead of chiplet-based designs, and high-performance integrated GPUs included all over the place. But their laptop and desktop processor lines have diverged a lot in recent years, with Ryzen 6000 laptop processors combining a 6nm version of Zen 3 called “Zen 3+”with an integrated GPU based on the RDNA2 architecture. This will continue for laptop Zen 4 processors, which will be manufactured on a 4nm process instead of a 5nm desktop process and will include an RDNA3-based GPU.
The rapid replacement of the Ryzen 6000’s RDNA2 GPU with an RDNA3 GPU is a sign that AMD is looking to improve the performance of its integrated graphics. AMD Ryzen laptop processors have been paired with some version of the company’s legacy Vega GPU architecture for years, and it’s good to see that we won’t be burdened with RDNA2-integrated GPUs long after AMD’s dedicated GPUs have bypassed it.
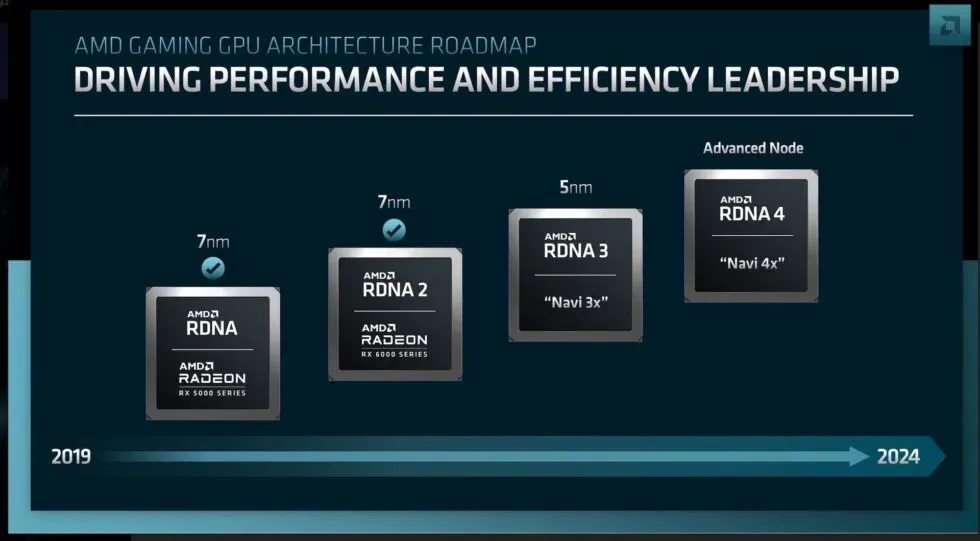
AMD also shared a few GPU-related details, confirming chipset-based designs for at least some of its next-gen 5nm RDNA3 GPUs, and scheduling an RDNA4 release in 2024 (on an as-yet undisclosed “advanced node”) . The company says RDNA3 GPUs will deliver 50% more performance per watt than RDNA2 through a combination of a new 5nm manufacturing process and architectural improvements.


